Epidermolysis bullosa
8. Otorhinolaringology
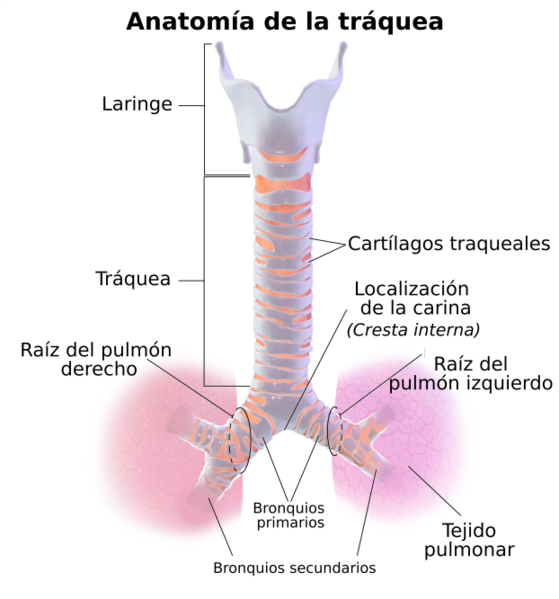
The thickening and scarring of the vocal cords manifests as a weak and hoarse cry and, in advanced cases, with aphonia (absence of voice). If, due to repetitive cicatrization, an airway narrowing happens (airway stenosis) the manifestations will be in the form of breathing difficulty and inspiratory stridor (high-pitched noise when breathing). It is essential to keep an eye on these complications, especially the stenosis, as very rarely they are associated to sudden death due to complete obstruction of the airway (due to the oedema, blisters, scarring tissue, etc.). We must be very alert of all the symptoms that might suggest an airway stenosis: inspiratorystridor, dysphonia, weakcry, etc. It is easier to detect these types of signals on children as the airway is smaller and its manifestation is clearer. In adolescents they can go more unnoticed due to the larynx and windpipe diameter increase. In cases of significant larynx stenosis, the insertion of a tracheostomy tube might be necessary to let an adequate breathing.