Dermatomiositis juvenil
Otros
2.1. Spirometry
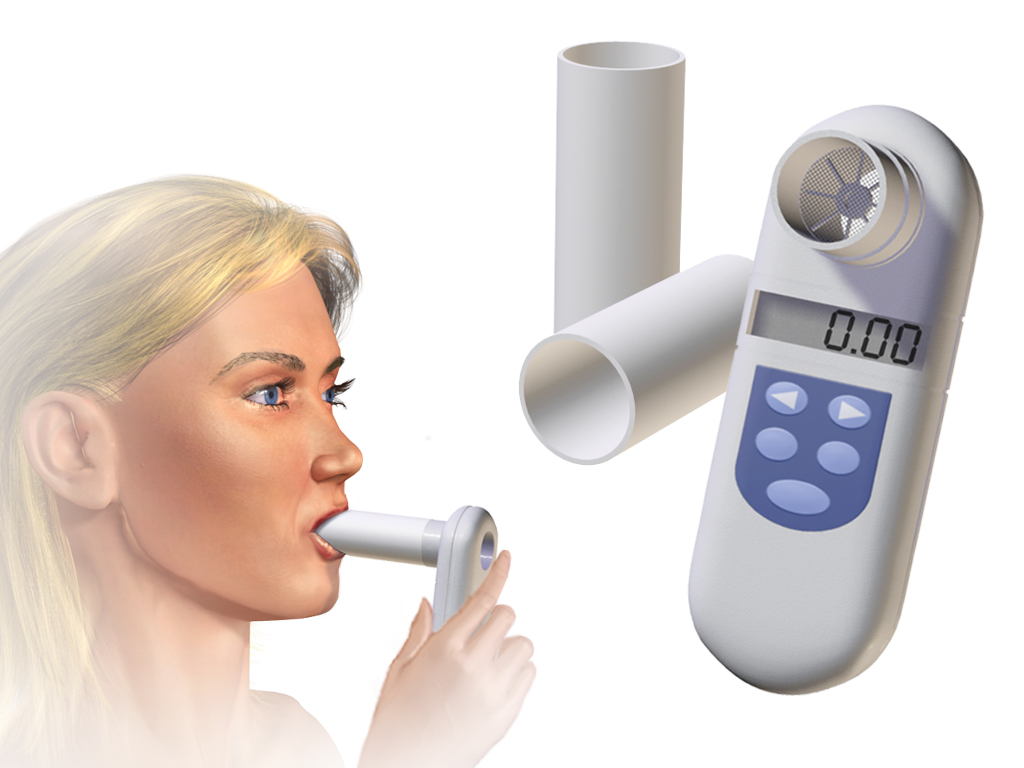
This is a non-invasive test that allows us to explore a person's respiratory function by measuring respiratory flows and volumes (i.e. the air that they are able to breathe in and out).
It consists of breathing through the mouth via a tube, forcing expiration to measure the flow of air out of the lungs. Since it requires the patient's cooperation, it is a test limited to older patients, usually above 5-6 years of age.
Spirometry does not tell us the cause of the lung disease, but shows us what type of breathing pattern the patient has: obstructive (air goes in well but cannot get out easily), restrictive (air cannot get in easily) or mixed (combines the two).
There are two types of spirometry:
- Simple spirometry: This consists of the person breathing slowly first, normally. Then they must take in and release as much air as they can. It measures, above all, lung volume and lung capacity (in specific parameters that we will not explain due to their complexity).
- Forced spirometry: the patient must take in as much air as possible and then release it abruptly until he/she cannot expel any more. Through this, we will know the forced volume and capacity, i.e., with the maximum expiration that the patient can perform.
Última modificación
Lun, 16/10/2023 - 09:23