Paediatric melanoma
What is cancer?
Cells are the building blocks that form tissue in the body. Genes are the instructions in cells for making new proteins, the functional unit that cells need to work. These regulatory elements will control how cells behave. Abnormal changes (mutations) in genes, losing some information in them or its dysfunctional can turn normal cells into cancer cells.
Cell division is a tightly controlled mechanism in which a cell will give place to two daughter cells. These new cells are made as the body needs them to replace injured or dying cells. This duplication is controlled by several proteins which will ensure the correct progression through the cell cycle (the process that the cell follows to duplicate). These proteins can be accelerators to progress through the cell cycle or can act as brakes to ensure giving time to the cell for correct duplication of the DNA and avoiding introducing mutations. Normal cells stay where they belong to and do not spread to other parts of the body. When normal cells grow old or get damaged, they die.
A cancer cell can duplicate extensively and without control because of two reasons: or the accelerator protein (protooncogene) has a mutation which happens to the impossibility of stopping them or the brake protein (tumour suppressor) has a mutation that does not allow them to work properly. Sometimes, both events can happen and in different proteins making it difficult to correct them with treatments.
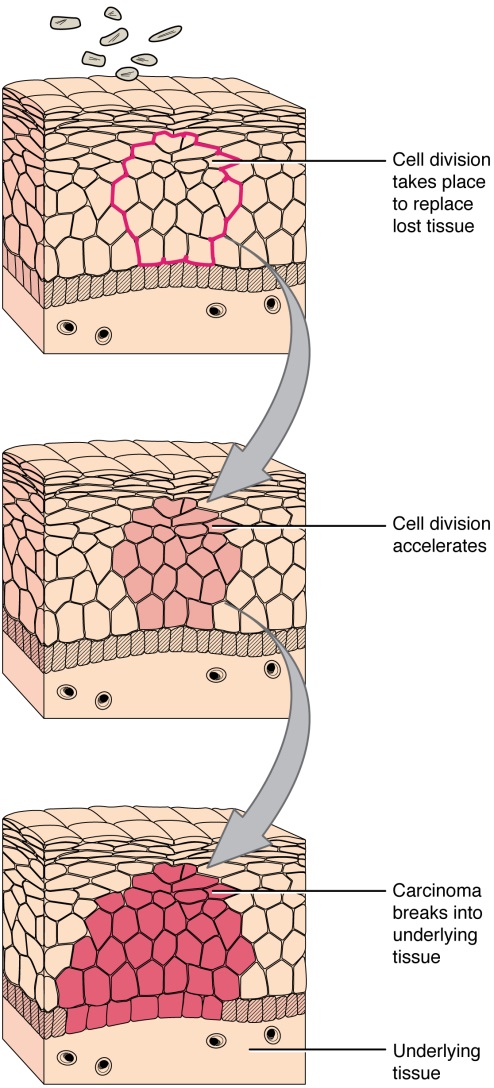
Cancer cells duplicate extensively until they produce a massive amount of cells. This stage of cancer called neoplasm is characterized by big amount of dead cells concentrated in a small place producing a mass with high levels of toxicity due to this accumulation of necrosis (dead cells by lack of nutrients). In this situation, cells that survive because their mechanisms for stopping are not working, divide enough to form a malignant tumour. The first tumour formed by the overgrowth of cancer cells is called the primary tumour. If they continue growing and dividing, cancer cells will not stay in place as they should and they will invade other tissues giving place to metastasis. Researchers are still learning what causes genes to mutate and cause cancer.
Cancer may occur anywhere in the body. There are five main types of cancer:
- Carcinomas originate in the skin or tissues that line the internal organs. Melanoma belongs to this group of cancers type.
- Sarcomas develop in the bone, cartilage, fat, muscle or other connective tissues.
- Leukaemia originates in the blood and bone marrow.
- Lymphomas start in the immune system.
- Central nervous system cancers develop in the brain and spinal cord.
Depending on the type of cell that is growing without control, the cancers will be named one or another way. The uncontrolled proliferation of melanocytes originates what scientists call melanoma.
DNA damage in skin cells is mainly caused by ultraviolet radiation from sunshine. It’s a slow process, involving the accumulation of many mutations to the point of affecting one gene or a group of genes triggering the uncontrolled proliferation of melanocytes. Also, inherited melanoma can be found when genetic mutations affect a family, generally by mutations in the tumour suppressor genes, making them not to work properly.