Gliomatosis cerebri
The brain and its cellular composition
The nervous system consists of excitable nerve cells (neurons), and synapses that form between the neurons and connect them to centres throughout the body or to other neurons. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Glia cells are found within tissues and are not excitable, but help with myelination, ionic regulation and extracellular fluid.
We can differentiate 3 types of glial cells: astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and microglia.
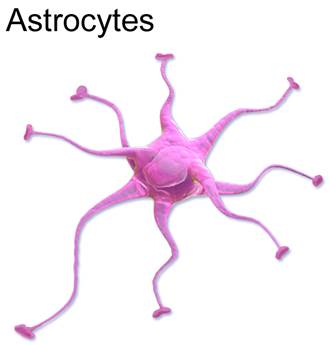
Astrocytes are named for their star-shaped morphology. Astrocytes are in intimate contact with the dendrites of the neuron and have ramifications (giving it the star shape).
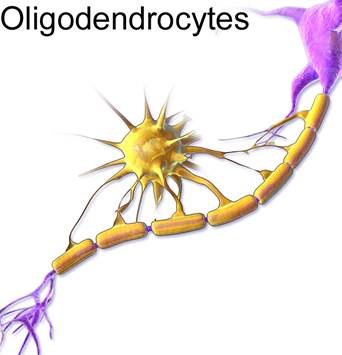
Oligodendrocytes give support to the neuron and protect the axons. They also help in the propagation of the nerve impulse.
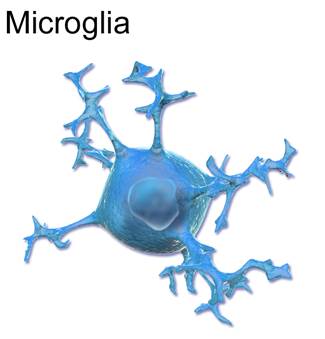
Cells of the Microglia are only found in the CNS and act as the immune system cells inside our brain. The microglia cells are activated in response to brain injury such as in inflammatory, neurodegenerative, neuro-inflammatory or traumatic processes.