Osteogenesis imperfecta
2.2. Hip
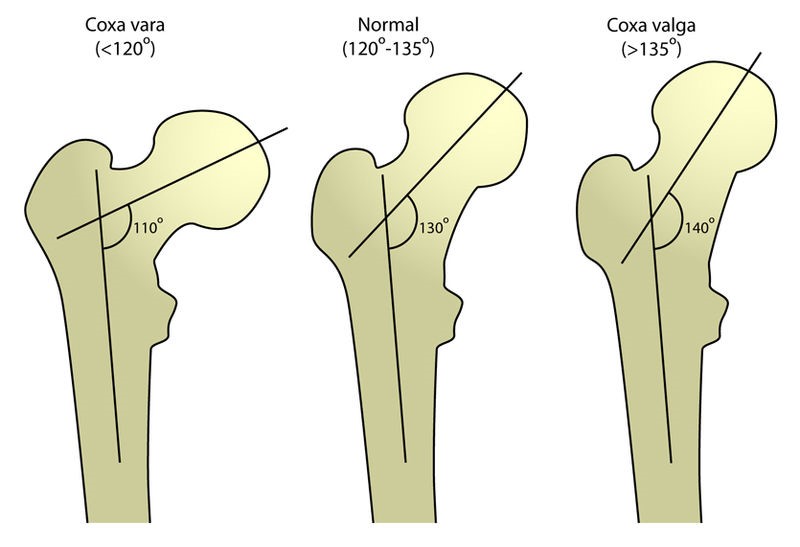
- Coxa vara: This hip deformity is characterised by a narrower angle formed between the diaphysis of the femur and a line crossing the head of the femur, deviating from the typical alignment (see Figures 12 and 13). It is a commonly observed deformity in people with osteogenesis imperfecta. Conversely, coxa valga, which involves a wider angle at the hip joint, also occurs in OI but is less common and generally associated with fewer complications.
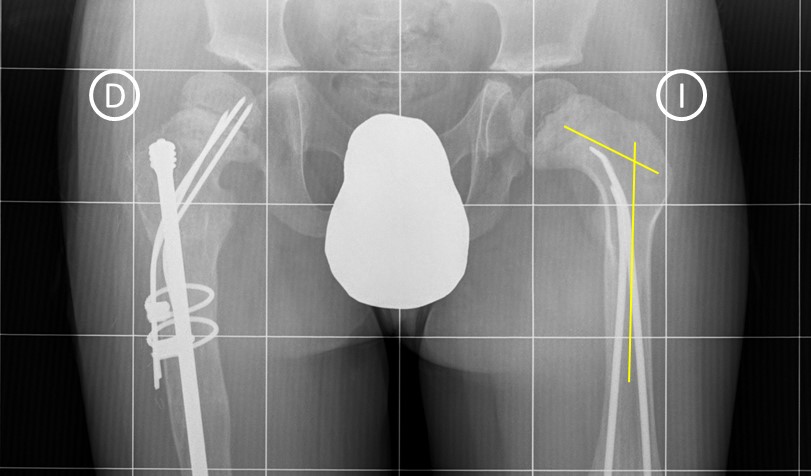
Coxa vara significantly impacts hip mobility and walking abilities. Moreover, this deformity alters the hip angle, increasing the susceptibility to fractures at the point of maximum flexion. The treatment for coxa vara and the optimal timing of intervention must be personalised for each patient. The most commonly employed surgical technique involves performing an osteotomy in the femoral neck to readjust its angle. To stabilise the structure, an endomedullary rod is inserted into the femur, accompanied by pins that traverse the neck of the bone. Additionally, supportive measures are implemented to maintain the bone and the inserted devices in their proper position.
Coxa valga can also manifest in individuals with OI, but it tends to have fewer associated complications. Nonetheless, it is important to monitor its progression through regular X-ray examinations.
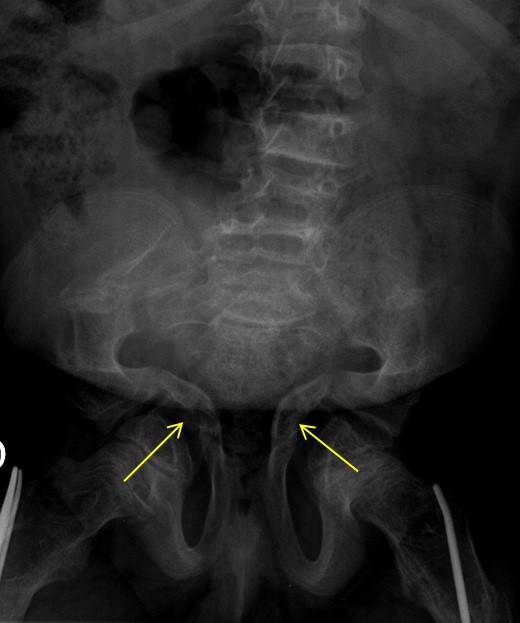
- Acetabular protrusion: This condition involves the hip joint protruding into the pelvic region (refer to Figure 14), where vital organs such as the intestines and bladder are situated. The compression exerted by the femoral head on these organs can lead to abdominal pain, constipation, and other related symptoms. Managing this complication is challenging, and current reported outcomes have been less than satisfactory. Generally, conservative approaches are employed, focusing on methods to regulate constipation. In severe cases, where intestinal obstruction hinders normal bowel movement, a colostomy may be required. A colostomy is a surgical procedure that redirects the terminal part of the intestine towards the abdominal wall, allowing for the elimination of faeces, which are collected in a bag attached to the abdomen.