Epidermolysis bullosa
4. EB types and classification
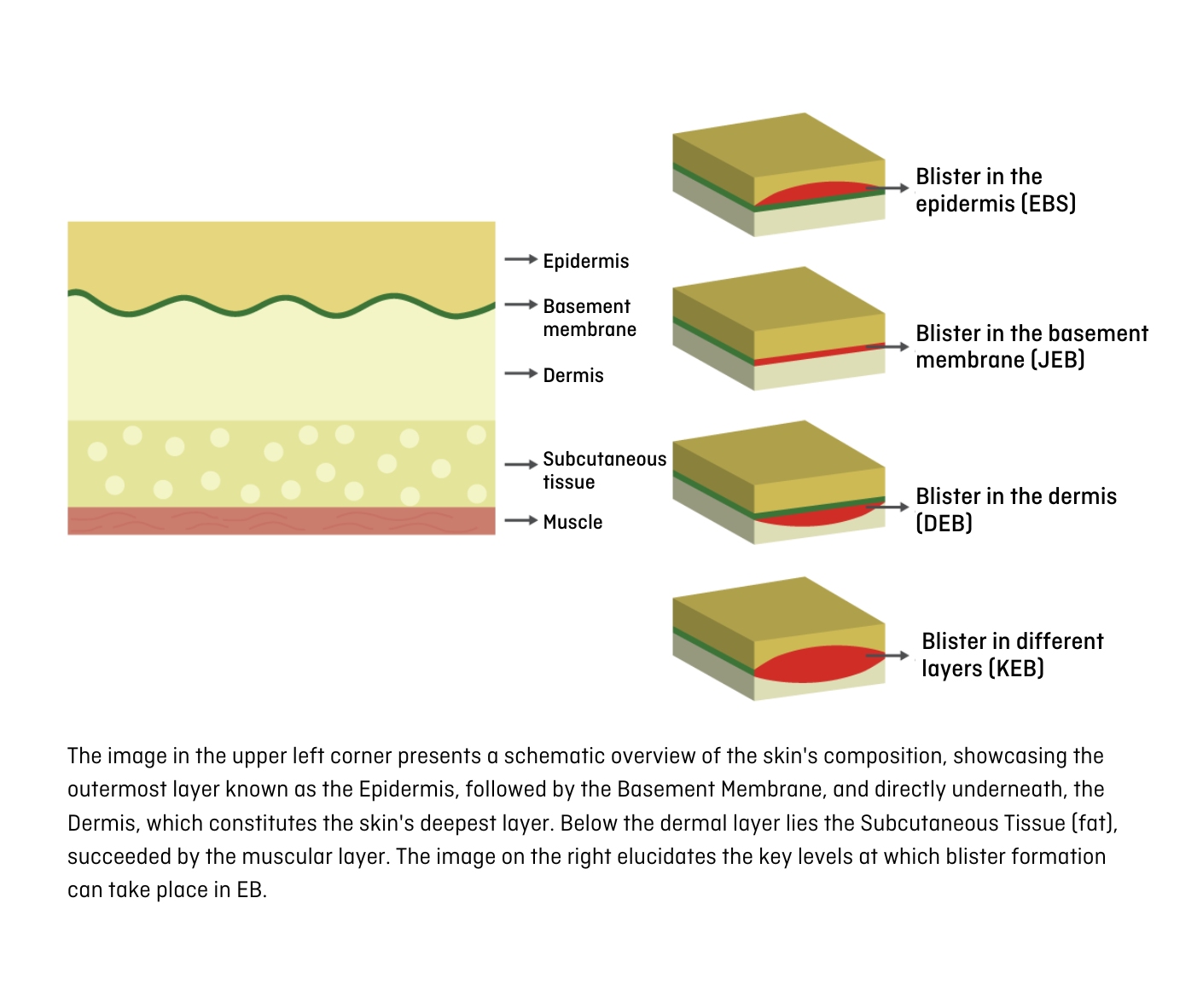
As previously stated in the introduction, the categorisation of EB into the 4 classical types relies on the site where blisters form within the distinct skin layers. Based on this location and the specific protein that is modified or missing, the subsequent typologies are established (Figure 6):
- Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex (EBS)
- Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB)
- Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB)
- Kindler Syndrome Epidermolysis Bullosa (KEB)
The disease is reclassified when new genes and clinical subtypes are identified. The information presented below regarding the classification of the four classical types and subtypes is based on the article published in February 2020, titled "Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility" (Has C., et al, 2020). With more than 30 subtypes, it becomes apparent that EB exhibits significant clinical heterogeneity. Furthermore, the disease spans a broad spectrum of severity. To ascertain the type and subtype of EB in newborns or individuals with milder symptoms, laboratory diagnostic tests are necessary. In the subsequent section, we will delve into the most prevalent subtypes.