Osteogenesis imperfecta
Others
3.2. Feet in OI
In people with osteogenesis imperfecta, the foot commonly exhibits laxity and flexibility, particularly in the forefoot area near the toes. This results in the appearance of a wide forefoot (refer to Figure 19). Additionally, there is often a minimal arch ("flat-footedness") and a tendency towards fallen arches, known as pes valgus (see Figure 20).
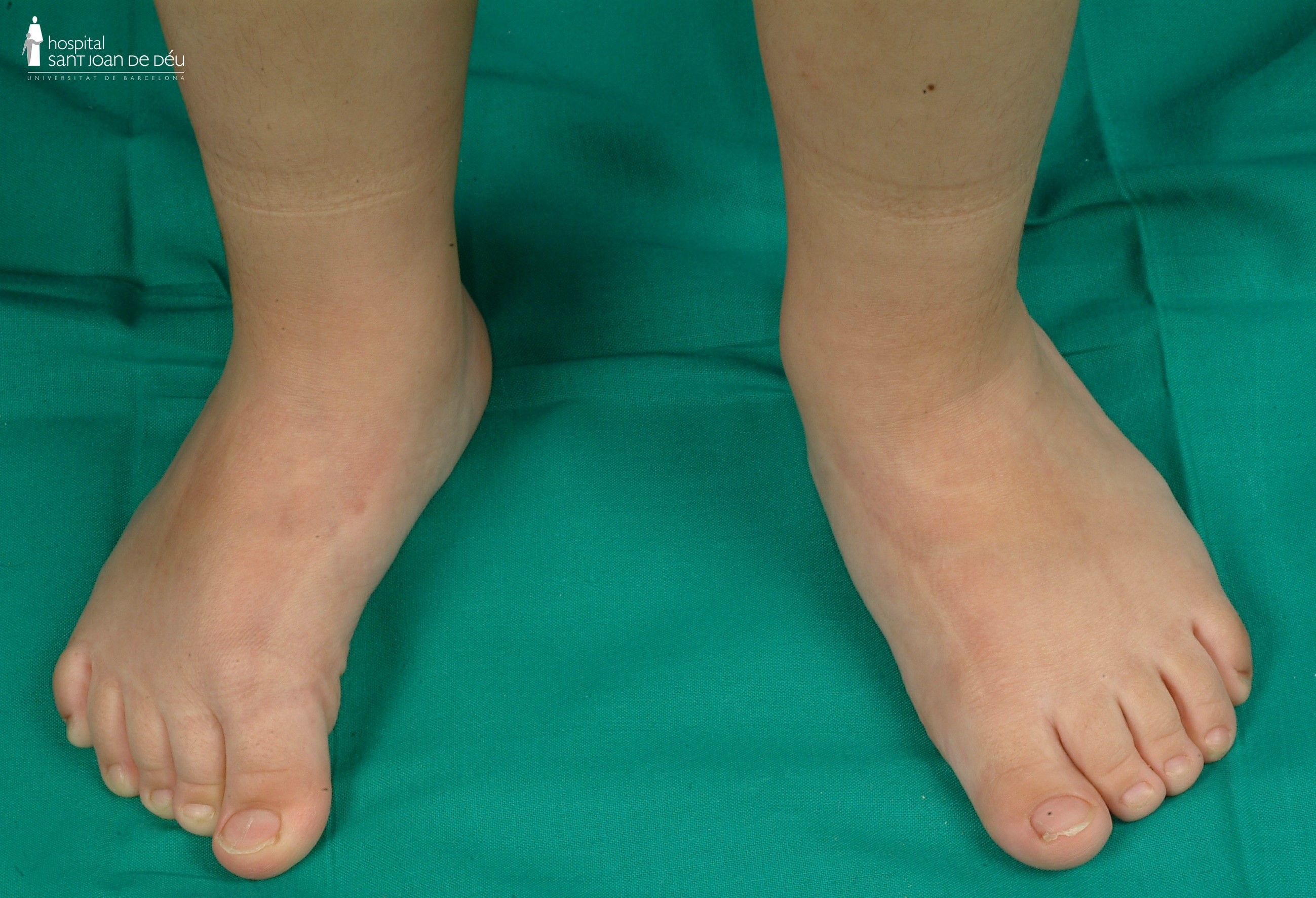
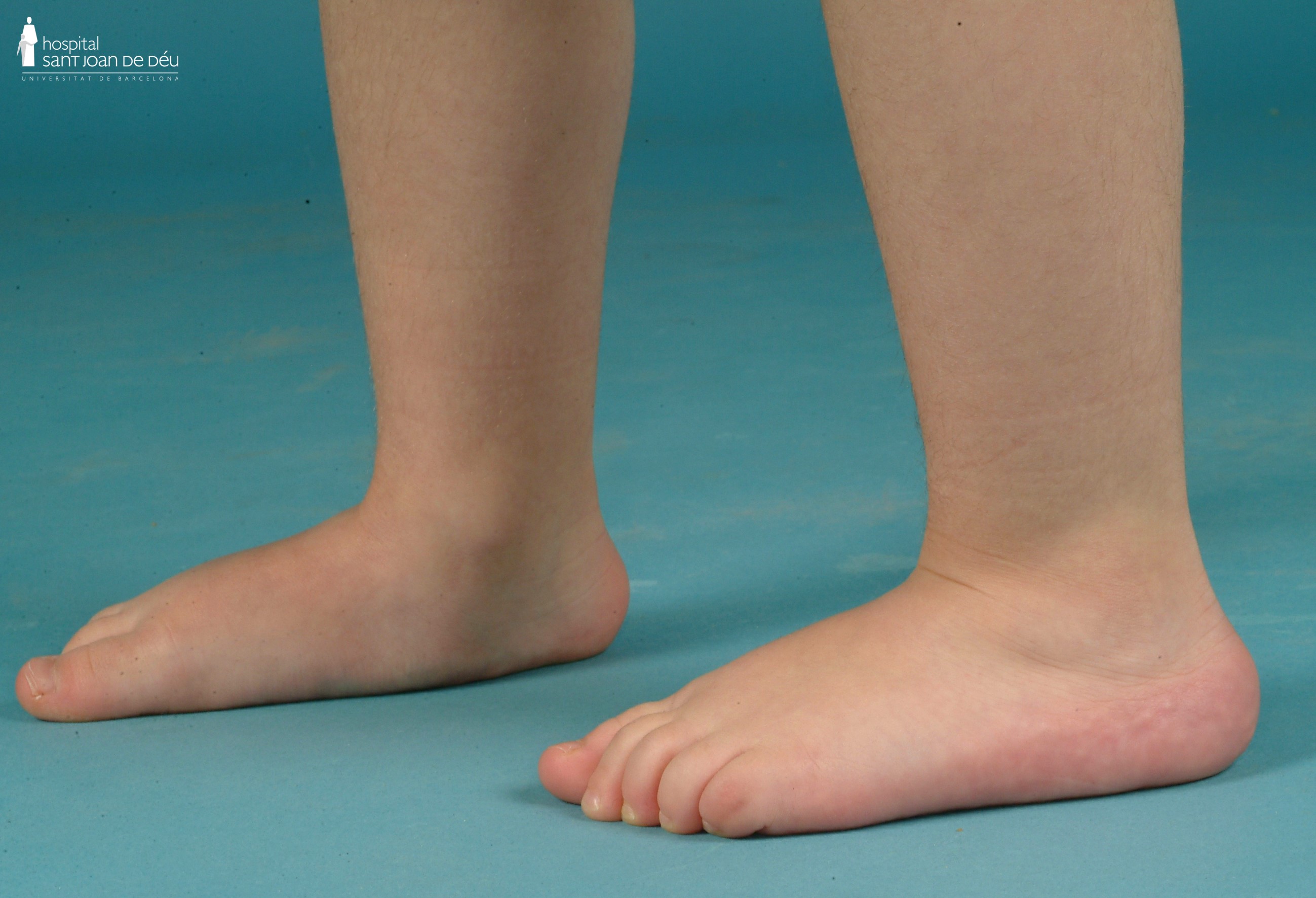
The management of the foot in osteogenesis imperfecta involves several approaches. Physiotherapy exercises are employed to strengthen the muscles surrounding the foot. Additionally, the use of inner sole inserts is recommended not to correct the foot's structure, but rather to provide support and alleviate any associated discomfort. Surgery is rarely considered, reserved for exceptional cases.
Last modified
27 June 2023