Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
What is leukaemia? And acute lymphoblastic leukaemia?
Leukaemia means “cancer of the blood”. In the blood there are different types of cells (like red blood cells, different white cells, and platelets). These cells develop from the so-called stem cells, that are produced in the bone marrow, which is the soft inner part of the bones.
The term "leukaemia" englobes a group of blood cancers that usually begin in this part of the body and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells called blasts or leukemia cells. These cells are immature and non-functional and grow out of control and prevent the rest of the blood cells from growing, causing diverse symptoms.
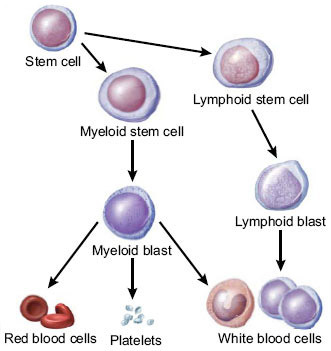
In the case of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL), cancer starts from a type of young white blood cell called lymphocyte, which, in normal conditions, would develop into mature white cells called B-cells or T-cells.
Check out further resources and websites for more information on this:
|
National Cancer Institute |
|
|
About childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) - GENERAL |
UK Cancer Research |
|
Children with Cancer UK |
|
|
American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) |
|
|
NHS |
|
|
Bloodwise |
|
|
About childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) - GENERAL |
UK Cancer Research |
|
The Nemours Foundation |
|
|
Children with Cancer UK |