Vascular anomalies
Others
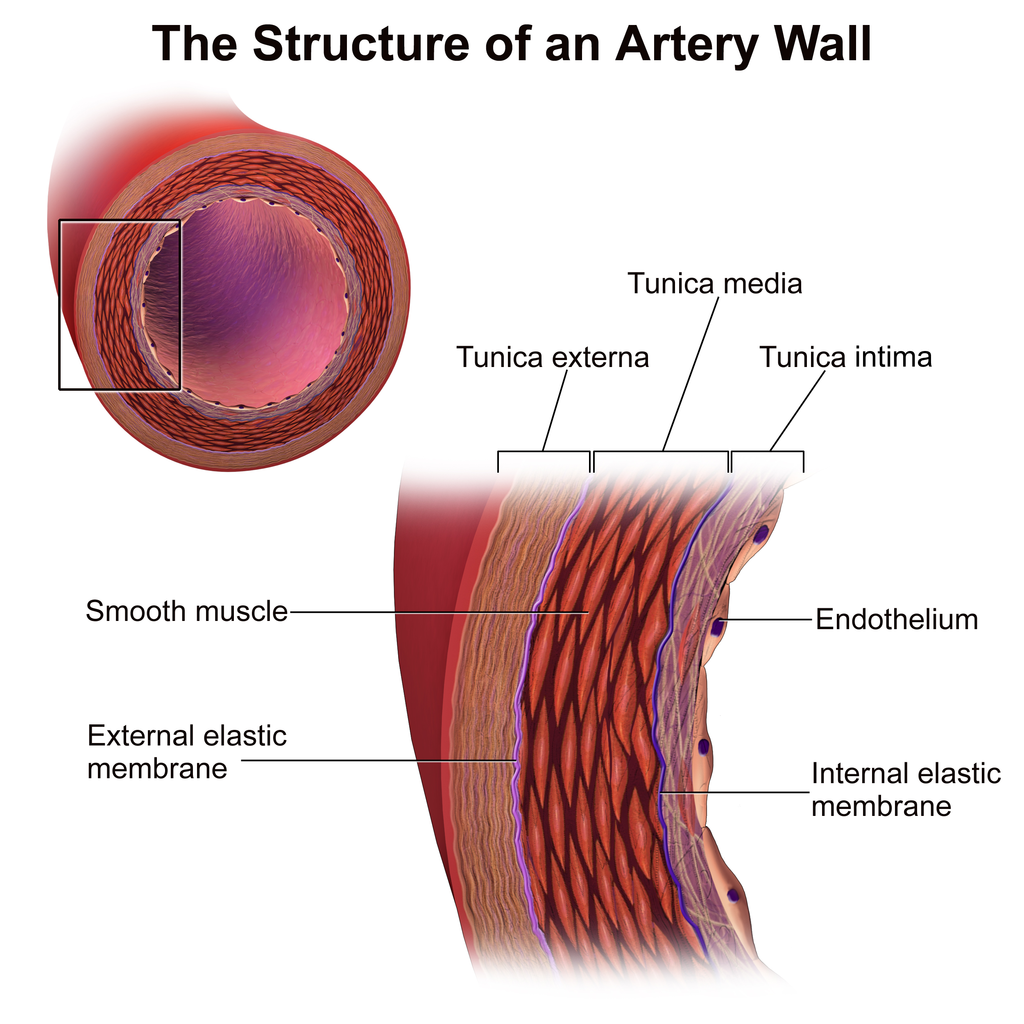
Layers of the circulatory system
From the outside to inside:
- Tunica externa: The outermost and thickest layer made out entirely of connective tissue fibres and surrounded by an elastic lamina.
- Tunica media: The middle layer. Composed of muscle cells, elastic and connective tissue. This layer is much bigger in arteries than veins, as arteries need muscle strength to contract to transport blood against resistance at an adequate pressure and for vasoconstriction in required situations (such as when you stand up after many hours laying down – when you wake up).
- Tunica intima: It is mostly made up of specialized cells known as endothelial cells (endothelium), which are distributed in one continuous layer and are supported by a sub-endothelial layer of connective tissue and support cells. These cells allow the exchange of substances between the bloodstream and tissues and prevent other substances from going inside or outside.
Last modified
17 December 2020