Epidermolysis bullosa
2. Basic research or discovery phase
Basic investigation is the one that chases knowledge of reality or nature phenomena to answer questions or so that said knowledge can be applied to other investigations. To better define it, we can see some of its fundamental characteristics:
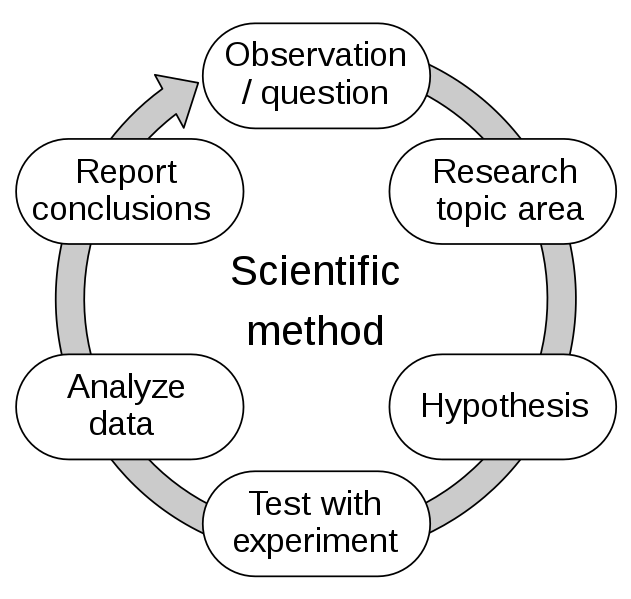
- Systematic: the scientific method (Figure 2) is used, with which after formulating a hypothesis, data is orderly and methodically collected to avoid bias, and they are analysed and interpreted to obtain conclusions.
- Objective: the results much be based on observed and measured facts.
- Precise and reproducible: the facts must be explained in an exact manner so that they can be reproduced by other people.
Basic investigation has an elevated economic cost. If we also add to it the time it takes to see its results, we could ask ourselves if it is worthwhile. Since it is an investigation destined to broaden the scientific knowledge without pursuing a practical application, it is difficult to see its value. However, it will be the fundament for any other science and most applied technique. In other words, there could not be clinical trials on humans without having scientific evidence first. This is given by basic investigation with studies on animals (preclinic). As it is well known, we cannot put the cart before the horse.
Thus, the development of new scientific knowledge is a long process with a very low success rate. But the discovery of a new drug or therapy is even more so. It is estimated that only 250 out of 10,000 compounds from the basic research stage make it to the preclinical (animal) research stage. And only 2% of drugs are approved and commercialized.