
Structural chromosomal abnormalities
Structural chromosomal abnormalities occur when a portion of a chromosome is missing, duplicated or rearranged in some way. Changes in chromosome structure can occur in different ways as we will discuss later.
These types of defects can be very subtle and difficult to detect in the lab. Even when a structural abnormality is found, it is difficult to predict what consequences it will have for the carrier. This can lead to frustrated parents, as they are in need to know as much as possible about their children's future.
In the field of clinical genetics, there is still much work to be done in order to ensure the highest correlation between the detected genetic abnormality and the symptoms to which it may be associated. In addition, it must be considered that epigenetics (changes that do not occur in the DNA sequence but that modify genetic expression) also play an important role in modifying people's genotype and phenotype.
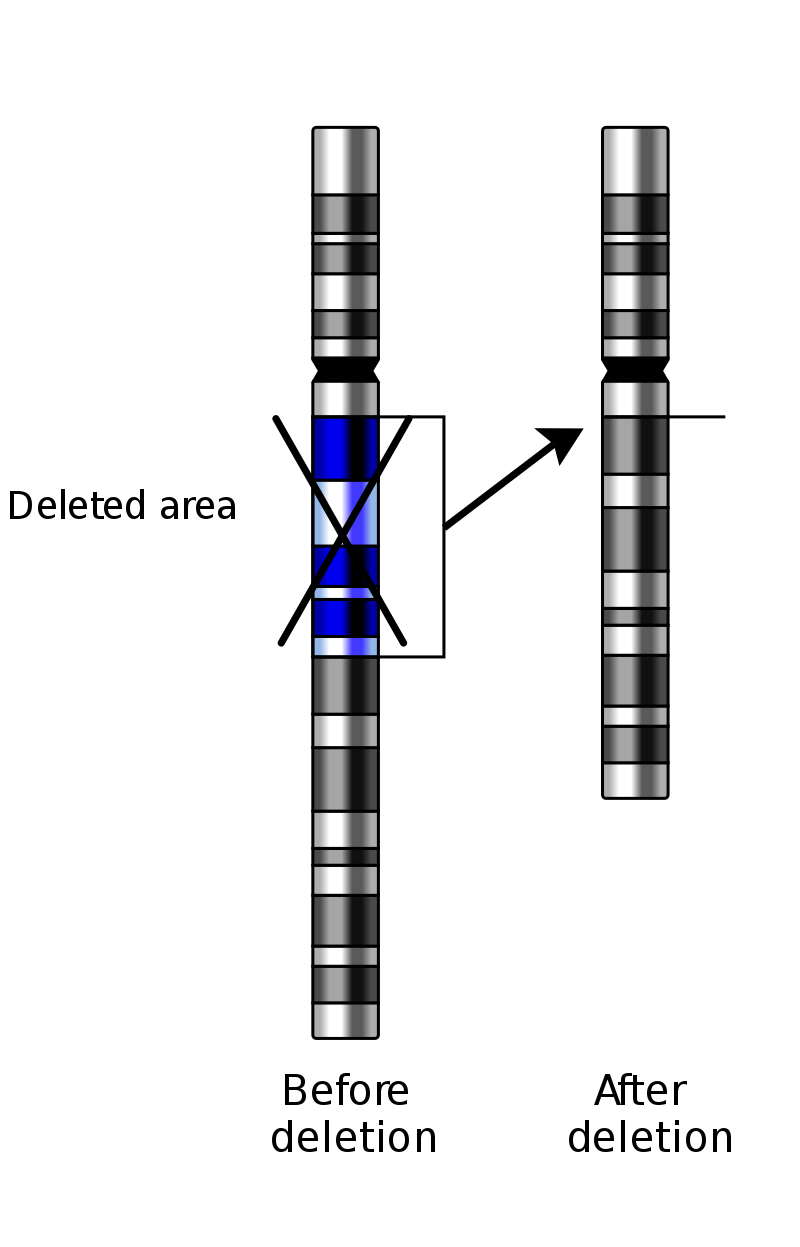
1. Deletions
In a chromosomal deletion a portion of the chromosome is missing or deleted. A deletion can occur on any chromosome and on any location and it can be of different sizes. If the material (the genes) missing contains important instructions for the body, the person affected may have learning difficulties, delayed development and severe health problems. The severity of these deletions will depend on the size of the deleted chromosome fragment and the place in the genome where the deletion has occurred.
2. Duplications
In chromosomal duplication, part of the chromosome is duplicated or has two copies. The result is additional chromosomal material. This extra chromosomal material can lead to gene malfunctioning, which may cause learning disabilities, developmental delays and health problems.
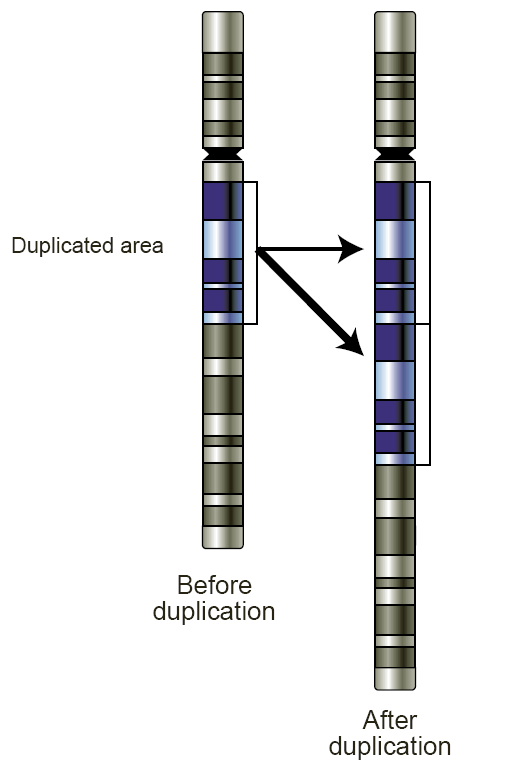
Schematic of a region of a chromosome before and after a duplication event (Wikimedia).
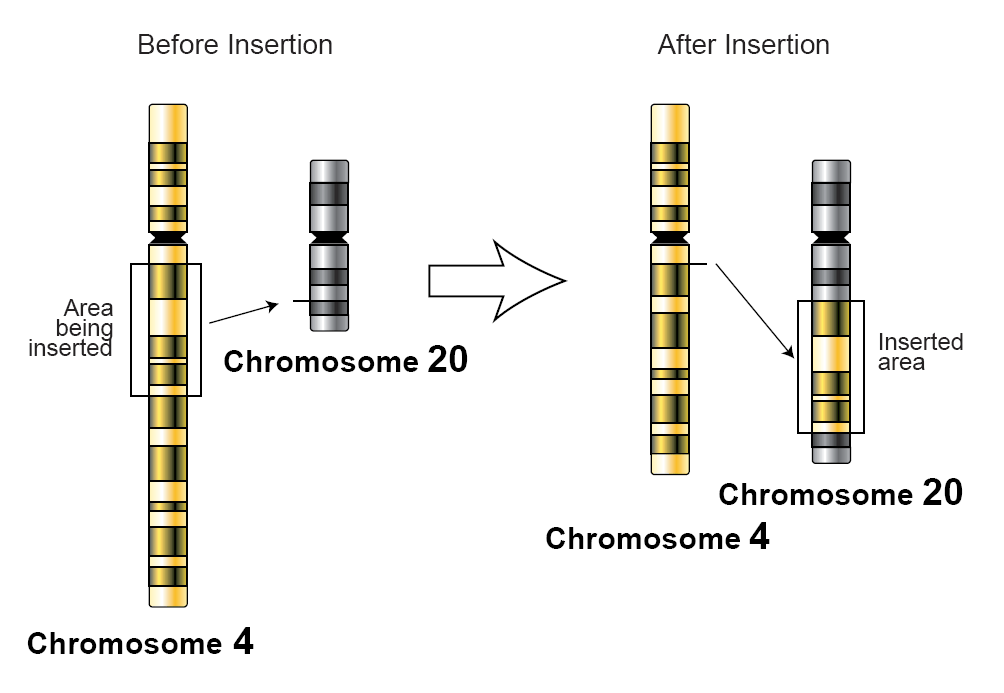
3. Insertions
In this type of chromosomal abnormality a portion of a chromosome has been inserted in an unusual position within the same or another chromosome. If there is no gain or loss of chromosome material, the person will be healthy. However, if there is gain or loss of chromosomal material, the person may have health problems.
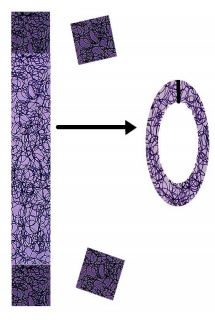
4. Ringing
A ring chromosome is a chromosome whose ends have fused together to form a ring. This usually occurs when the ends of the same chromosome have experienced a deletion. The ends that remain are “sticky” and that is why they come together to form a ring. The effect of this anomaly usually depends on how much material and what "information" was deleted before the ring was formed.
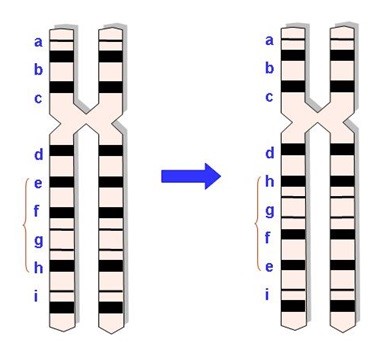
5. Inversions
Chromosome inversion are defined as a rearrangement produced by two break-points within the same chromosome. In most cases, this does not have health implications.
6. Translocations
We will cover this type of anomaly in the next blogpost.
Consequences of structural chromosomal abnormalities
If a parent has a chromosomal abnormality, will they always pass it on to their offspring?
Not necessarily. There are several possibilities for each pregnancy:
- The child may inherit only completely normal chromosomes.
- The child may inherit the same chromosomal abnormality the father/mother has.
- The child may be born with developmental delays, learning disabilities and health problems.
- The pregnancy may end in an abortion.
It is quite possible for a person with a chromosomal abnormality to have completely healthy children, and, in fact, many of these people do. Each anomaly is unique and carriers should discuss their particular situation with a medical geneticist.
Tests to detect chromosomal abnormalities
The genetic test to find out if a person is a carrier of a chromosomal abnormality is based on a simple blood test. Blood cells are carefully examined in the laboratory and scientists look for chromosome location and structure. This test is called a karyotype analysis. Also, it is possible to run a test during pregnancy to find out if the baby has a chromosomal abnormality. This test is called prenatal diagnosis. It is recommended to discuss the different scenarios with a genetic counselor.
What about other family members?
If a person finds out that he/she is a carrier of a chromosomal abnormality, it is convenient to inform other members of their family. This will give them the opportunity to aks for a blood test to see if they are also carriers of the abnormality. This information may be important to family members who have children or who are thinking of having children in the future. If they are not carriers of the chromosomal abnormality, they will not be able to pass it on to their children, but if they are carriers, they might consider getting a test during pregnancy to check their baby's chromosomes.
Some people find it difficult to talk about such things with their family, sometimes because are afraid of causing anxiety and other times because they are not in touch with their relatives. This can be solved by genetic specialists, as they have a lot of experience in dealing with families and these kind of situations.
To wrap up
- A chromosomal abnormality can be inherited either from one parent or occur at the time of conception.
- A chromosomal abnormality cannot be corrected. It is present throughout life.
- A chromosome abnormality is not something that can be transmitted to another person like a virus or bacteria. Thus, a carrier of a chromosomal abnormality can be a blood donor.
- Many people with chromosomal abnormalities have healthy children.
