Kabuki syndrome
1. The structure of the heart
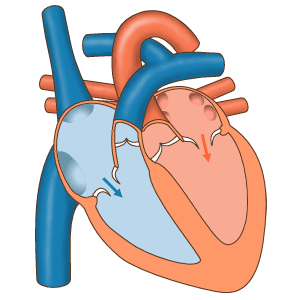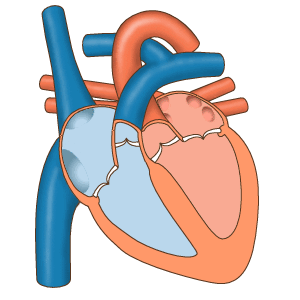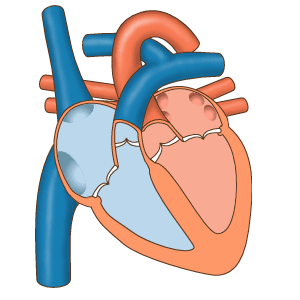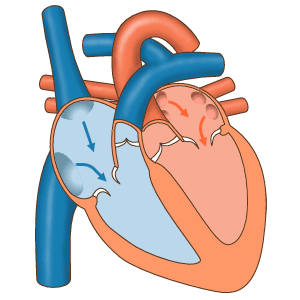
The structure of the heart
The heart is a muscle. It is the main muscular organ of the circulatory system.
In humans, the heart is a hollow muscle located in the thoracic cavity between the lungs and slightly to the left. It functions as a suction and propulsive pump, delivering blood throughout the body.
The heart is contained in a protective sac called the pericardium, which normally contains a small amount of fluid.
The heart is divided into four chambers or cavities:
-
The two that receive blood are called the atria: right atrium and left atrium.
-
The two that propel the blood are called ventricles: right ventricle and left ventricle.
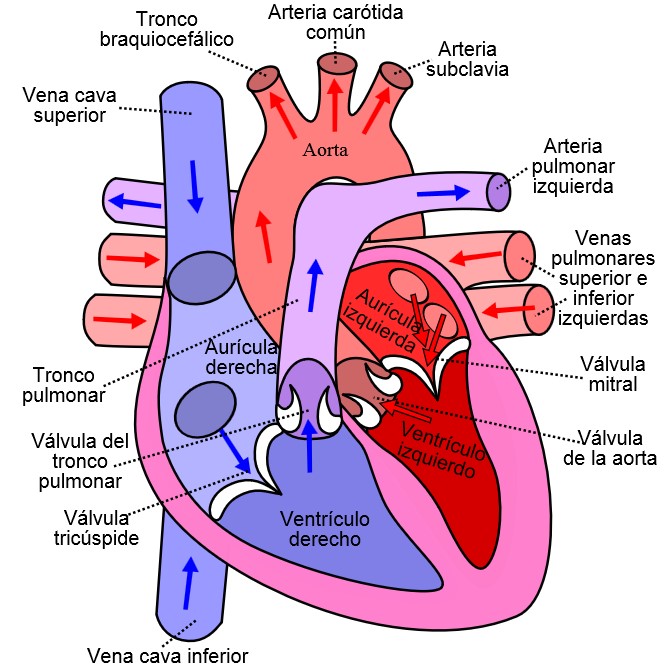
The heart is a self-controlled muscular organ. By itself it can initiate each cardiac cycle with its contraction and relaxation. It is made up of two parallel pumps that work in coordination to propel blood to all the organs and tissues of the body.