Kabuki syndrome
1. The eye
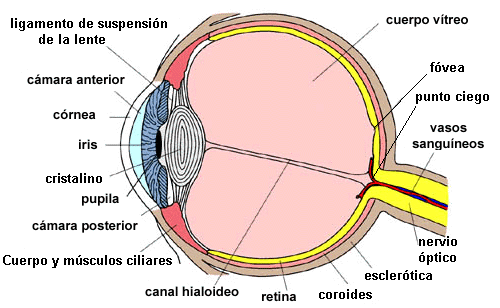
The eye is a complex organ responsible for the sense of sight (Figure 1). The ocular system is a complex structure made up of three closely related components:
1. The optical part consists of the lenses and media that allow the objects we see to be properly projected onto the retina (well-focused and at the right size). It is primarily composed of the cornea, sclera, iris, ciliary muscle, aqueous humor, lens, and vitreous humor. All of these must be transparent to function effectively.
2. The "electrical" part includes:
a) The retina, which acts as the “photographic film” of the visual system, where images are projected and then transmitted to the brain. It is located at the back of the eye.
b) The nerves and nerve pathways, which serve as the “wires” that transmit images from the retina to the visual cortex (in the brain).
c) The visual cortex, found at the back of the brain, is where the images captured by our eyes are interpreted. It acts as the “computer” that enables us to recognize, for example, that the round object we see is a ball or that the white spot in the sky is a cloud.
3. The motor part is responsible for coordinating eye movement when we want to look at an object. It consists of:
a) The brain: the frontal part of the brain (the frontal cortex) controls voluntary eye movements, while two structures located at its base and back (the brainstem and cerebellum) manage the involuntary coordination of these movements.
b) The nerves responsible for eye mobility, which operate through the muscles: specifically, cranial nerves III, IV, and VI.
c) The extraocular muscles: these are the muscles that surround the eyes and allow them to move in any direction.